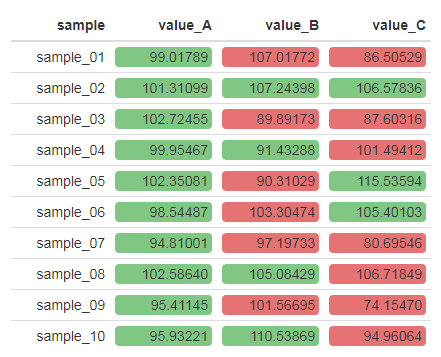
Formattable is a powerful R library used to format tables. There are many built-in functions which allow a user to style tables using color, bars ad icons. In addition you can create your own custom formatters. Below is an example of how to color a data frame using information from a second data frame. Average values are colored red if the RSD is greater than 0.15 and green if it is below.
This was developed in order to represent a large table of data color-coded accordng to RSD so that the analyst could quickly identify potential sources of systematic error.
table of data

table of RSDs
table of data color-coded according to RSDs
Code
library(dplyr)
library(tidyr)
library(formattable)
## generate some dummy data
df_dummy <- data.frame(sample = rep(sprintf('sample_%02i', 1:10), 4),
value_A = rnorm(40, 100, 5),
value_B = rnorm(40, 100, 15),
value_C = rnorm(40, 100, 25),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
## calculate stats
df_stats <- df_dummy %>%
gather(ref, value, -sample) %>%
group_by(sample, ref) %>%
summarise(avg = mean(value),
stdev = sd(value)) %>%
mutate(rsd = stdev / avg)
## pull out a table of average results
df_avg <- df_stats %>%
select(sample, ref, avg) %>%
spread(ref, avg)
## pull out a table of RSDs
df_rsd <- df_stats %>%
select(sample, ref, rsd) %>%
spread(ref, rsd)
## create a series of formatters, one for each data column
fmt <- lapply(1:(ncol(df_rsd)-1), function(y) {
d <- df_rsd[[y + 1]]
colors <- sapply(d, function(x) ifelse(x <= 0.15, '#81C784', '#e57373'))
formatter("span",
style = style(display = 'block',
padding = '0 4px',
`border-radius` = '4px',
`background-color` = colors))
})
## name list items
l.fmt <- setNames(lapply(1:(ncol(df_avg)-1), function(x) fmt[[x]]), names(df_avg)[2:ncol(df_avg)])
## create table
formattable(df_avg, l.fmt)